NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE – NMR
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a spectroscopic technique that enables the characterization and structural elucidation of organic compounds in liquid or solid state. It uses radiation in the low energy radio frequency band, which can cause nuclear spin transitions in the presence of a magnetic field.
The technique has high sensitivity in differentiating similar atoms due to differences in the electronic shielding of their nuclei, enabling the identification of position and ligands in the characterization of molecular structures. Used mainly in the identification of carbon-hydrogen structures, the most used types are H1 NMR and C13 NMR.
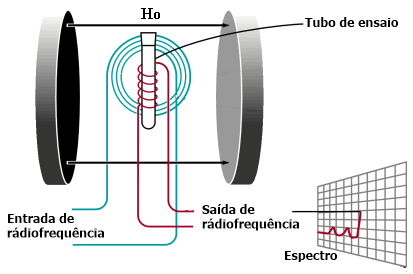
The interest in this technique in the industry has grown due to its efficiency and specific instrumentation capacity for the analysis of solid samples.
